92. Reverse Linked List II


Description
Given the head of a singly linked list and two integers left and right where left <= right, reverse the nodes of the list from position left to position right, and return the reversed list.
Example 1:
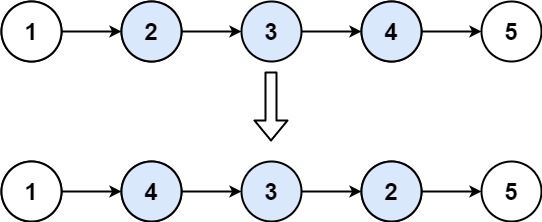
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4 Output: [1,4,3,2,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [5], left = 1, right = 1 Output: [5]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
n. 1 <= n <= 500-500 <= Node.val <= 5001 <= left <= right <= n
Follow up: Could you do it in one pass?
Solution
reverse-linked-list-ii.py
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head: ListNode, left: int, right: int) -> ListNode:
if left == right: return head
dummy = ListNode(-1, head)
prev, curr = dummy, head
for _ in range(left - 1):
prev = prev.next
curr = curr.next
res = None
for _ in range(right - left + 1):
temp = curr.next
curr.next = res
res = curr
curr = temp
prev.next.next = curr
prev.next = res
return dummy.next
reverse-linked-list-ii.cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
if (m == n) return head;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode *curr = head, *prev = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++){
curr = curr->next;
prev = prev->next;
}
ListNode *temp = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < n-m+1; i++){
ListNode* next = curr->next;
curr->next = temp;
temp = curr;
curr = next;
}
prev->next->next = curr;
prev->next = temp;
return dummy->next;
}
};