834. Sum of Distances in Tree


Description
There is an undirected connected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1 and n - 1 edges.
You are given the integer n and the array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Return an array answer of length n where answer[i] is the sum of the distances between the ith node in the tree and all other nodes.
Example 1:
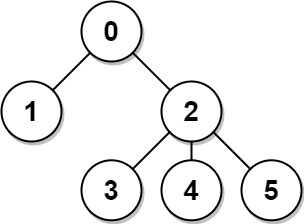
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[2,4],[2,5]] Output: [8,12,6,10,10,10] Explanation: The tree is shown above. We can see that dist(0,1) + dist(0,2) + dist(0,3) + dist(0,4) + dist(0,5) equals 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8. Hence, answer[0] = 8, and so on.
Example 2:

Input: n = 1, edges = [] Output: [0]
Example 3:
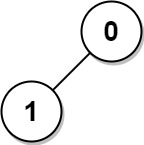
Input: n = 2, edges = [[1,0]] Output: [1,1]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 3 * 104edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != bi- The given input represents a valid tree.
Solution
sum-of-distances-in-tree.py
class Solution:
def sumOfDistancesInTree(self, N, edges):
tree = collections.defaultdict(set)
res = [0] * N
count = [1] * N
for i, j in edges:
tree[i].add(j)
tree[j].add(i)
def dfs(root, pre):
for i in tree[root]:
if i != pre:
dfs(i, root)
count[root] += count[i]
res[root] += res[i] + count[i]
def dfs2(root, pre):
for i in tree[root]:
if i != pre:
res[i] = res[root] - count[i] + N - count[i]
dfs2(i, root)
dfs(0, -1)
dfs2(0, -1)
return res