850. Rectangle Area II


Description
You are given a 2D array of axis-aligned rectangles. Each rectangle[i] = [xi1, yi1, xi2, yi2] denotes the ith rectangle where (xi1, yi1) are the coordinates of the bottom-left corner, and (xi2, yi2) are the coordinates of the top-right corner.
Calculate the total area covered by all rectangles in the plane. Any area covered by two or more rectangles should only be counted once.
Return the total area. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
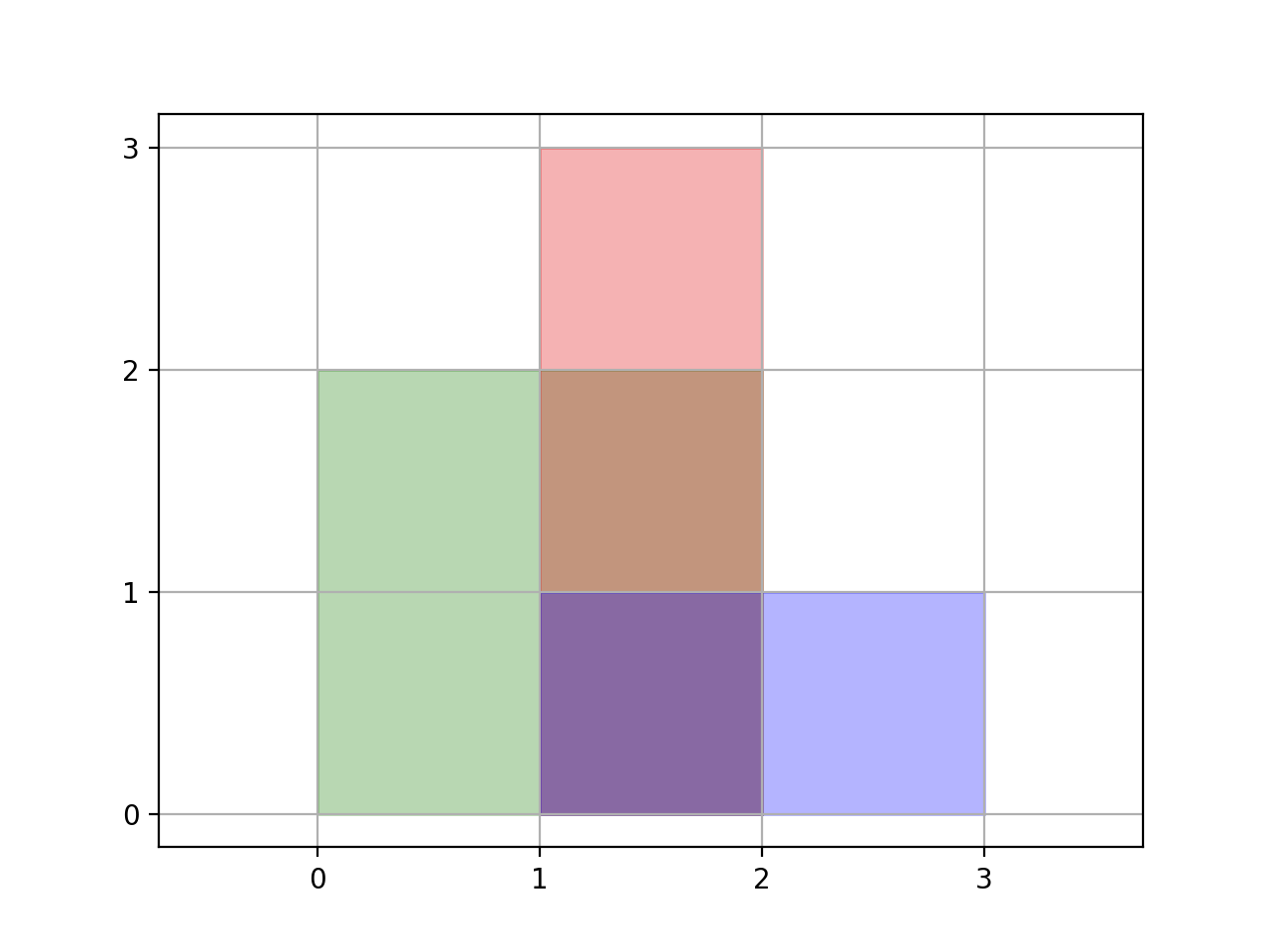
Input: rectangles = [[0,0,2,2],[1,0,2,3],[1,0,3,1]] Output: 6 Explanation: A total area of 6 is covered by all three rectangles, as illustrated in the picture. From (1,1) to (2,2), the green and red rectangles overlap. From (1,0) to (2,3), all three rectangles overlap.
Example 2:
Input: rectangles = [[0,0,1000000000,1000000000]] Output: 49 Explanation: The answer is 1018 modulo (109 + 7), which is 49.
Constraints:
1 <= rectangles.length <= 200rectanges[i].length == 40 <= xi1, yi1, xi2, yi2 <= 109
Solution
rectangle-area-ii.py
class Solution:
def rectangleArea(self, rectangles: List[List[int]]) -> int:
M = 10 ** 9 + 7
recList = []
def mergeRec(recList, curr, i):
if len(recList) <= i:
recList.append(curr)
return
r = recList[i]
if curr[2] <= r[0] or curr[3] <= r[1] or curr[0] >= r[2] or curr[1] >= r[3]:
mergeRec(recList, curr, i + 1)
return
if curr[0] < r[0]:
mergeRec(recList, [curr[0], curr[1], r[0], curr[3]], i + 1)
if curr[2] > r[2]:
mergeRec(recList, [r[2], curr[1], curr[2], curr[3]], i + 1)
if curr[1] < r[1]:
mergeRec(recList, [max(curr[0], r[0]), curr[1], min(curr[2], r[2]), r[1]], i + 1)
if curr[3] > r[3]:
mergeRec(recList, [max(curr[0], r[0]), r[3], min(curr[2], r[2]), curr[3]], i + 1)
for rec in rectangles:
mergeRec(recList, rec, 0)
res = 0
for (x1, y1, x2, y2) in recList:
res += (x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1)
return res % M