1028. Recover a Tree From Preorder Traversal


Description
We run a preorder depth-first search (DFS) on the root of a binary tree.
At each node in this traversal, we output D dashes (where D is the depth of this node), then we output the value of this node. If the depth of a node is D, the depth of its immediate child is D + 1. The depth of the root node is 0.
If a node has only one child, that child is guaranteed to be the left child.
Given the output traversal of this traversal, recover the tree and return its root.
Example 1:
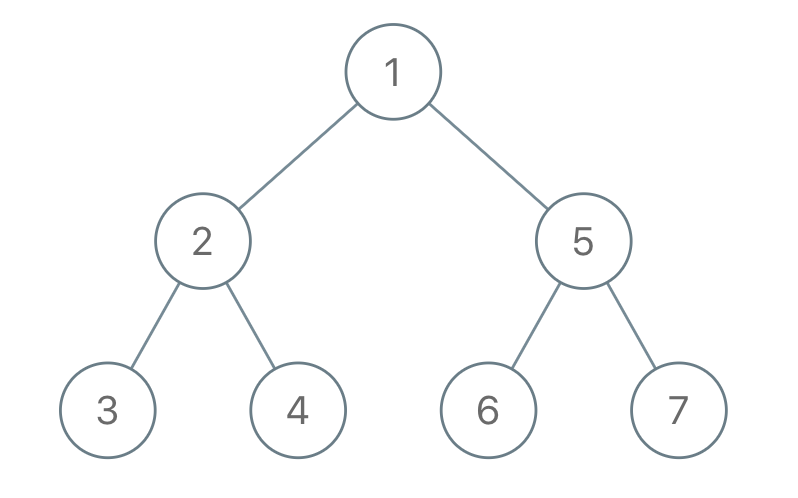
Input: traversal = "1-2--3--4-5--6--7" Output: [1,2,5,3,4,6,7]
Example 2:
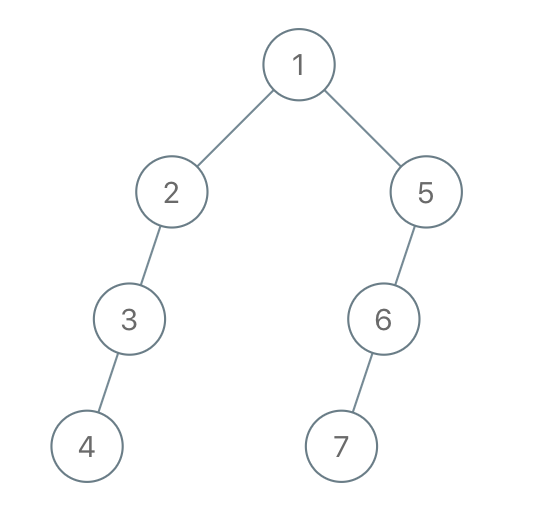
Input: traversal = "1-2--3---4-5--6---7" Output: [1,2,5,3,null,6,null,4,null,7]
Example 3:
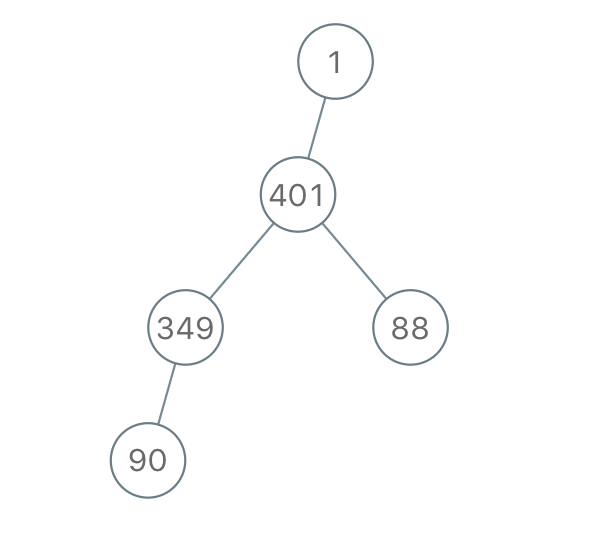
Input: traversal = "1-401--349---90--88" Output: [1,401,null,349,88,90]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the original tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. 1 <= Node.val <= 109
Solution
recover-a-tree-from-preorder-traversal.py
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def recoverFromPreorder(self, A: str) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
stack = []
n = len(A)
index = 0
while index < n:
depth = 0
while index < n and A[index] == '-':
depth += 1
index += 1
val = 0
while index < n and A[index].isdigit():
val = val * 10 + int(A[index])
index += 1
while len(stack) > depth:
stack.pop()
node = TreeNode(val)
if stack:
if not stack[-1].left:
stack[-1].left = node
else:
stack[-1].right = node
stack.append(node)
while len(stack) > 1:
stack.pop()
return stack.pop()