1110. Delete Nodes And Return Forest


Description
Given the root of a binary tree, each node in the tree has a distinct value.
After deleting all nodes with a value in to_delete, we are left with a forest (a disjoint union of trees).
Return the roots of the trees in the remaining forest. You may return the result in any order.
Example 1:
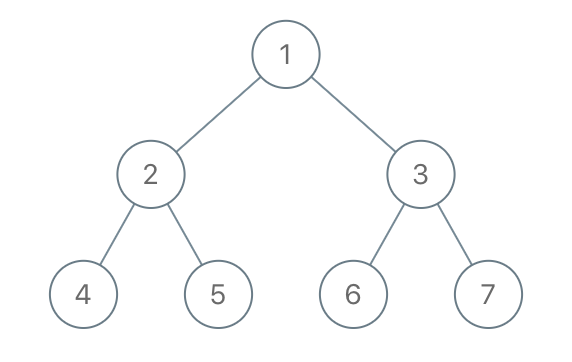
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], to_delete = [3,5] Output: [[1,2,null,4],[6],[7]]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,4,null,3], to_delete = [3] Output: [[1,2,4]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree is at most
1000. - Each node has a distinct value between
1and1000. to_delete.length <= 1000to_deletecontains distinct values between1and1000.
Solution
delete-nodes-and-return-forest.py
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def delNodes(self, root: TreeNode, to_delete: List[int]) -> List[TreeNode]:
res = []
delete = set(to_delete)
def dfs(node, is_root):
if not node: return None
to_delete = node.val in delete
if is_root and not to_delete:
res.append(node)
node.left = dfs(node.left, to_delete)
node.right = dfs(node.right, to_delete)
return None if to_delete else node
dfs(root, True)
return res