1261. Find Elements in a Contaminated Binary Tree


Description
Given a binary tree with the following rules:
root.val == 0- If
treeNode.val == xandtreeNode.left != null, thentreeNode.left.val == 2 * x + 1 - If
treeNode.val == xandtreeNode.right != null, thentreeNode.right.val == 2 * x + 2
Now the binary tree is contaminated, which means all treeNode.val have been changed to -1.
Implement the FindElements class:
FindElements(TreeNode* root)Initializes the object with a contaminated binary tree and recovers it.bool find(int target)Returnstrueif thetargetvalue exists in the recovered binary tree.
Example 1:
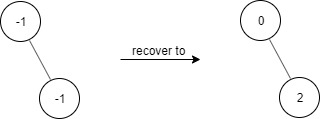
Input ["FindElements","find","find"] [[[-1,null,-1]],[1],[2]] Output [null,false,true] Explanation FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,null,-1]); findElements.find(1); // return False findElements.find(2); // return True
Example 2:
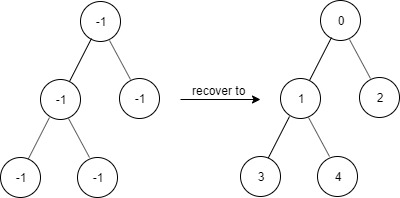
Input ["FindElements","find","find","find"] [[[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]],[1],[3],[5]] Output [null,true,true,false] Explanation FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]); findElements.find(1); // return True findElements.find(3); // return True findElements.find(5); // return False
Example 3:
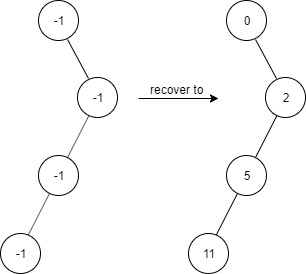
Input ["FindElements","find","find","find","find"] [[[-1,null,-1,-1,null,-1]],[2],[3],[4],[5]] Output [null,true,false,false,true] Explanation FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,null,-1,-1,null,-1]); findElements.find(2); // return True findElements.find(3); // return False findElements.find(4); // return False findElements.find(5); // return True
Constraints:
TreeNode.val == -1- The height of the binary tree is less than or equal to
20 - The total number of nodes is between
[1, 104] - Total calls of
find()is between[1, 104] 0 <= target <= 106
Solution
find-elements-in-a-contaminated-binary-tree.py
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class FindElements:
def __init__(self, root: TreeNode):
root.val = 0
self.s = set()
self.build(root)
def find(self, target: int) -> bool:
return target in self.s
def build(self, root):
if not root: return
if root.left:
root.left.val = root.val*2 + 1
self.s.add(root.left.val)
self.build(root.left)
if root.right:
root.right.val = root.val*2 + 2
self.s.add(root.right.val)
self.build(root.right)
# Your FindElements object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = FindElements(root)
# param_1 = obj.find(target)