1325. Delete Leaves With a Given Value


Description
Given a binary tree root and an integer target, delete all the leaf nodes with value target.
Note that once you delete a leaf node with value target, if its parent node becomes a leaf node and has the value target, it should also be deleted (you need to continue doing that until you cannot).
Example 1:
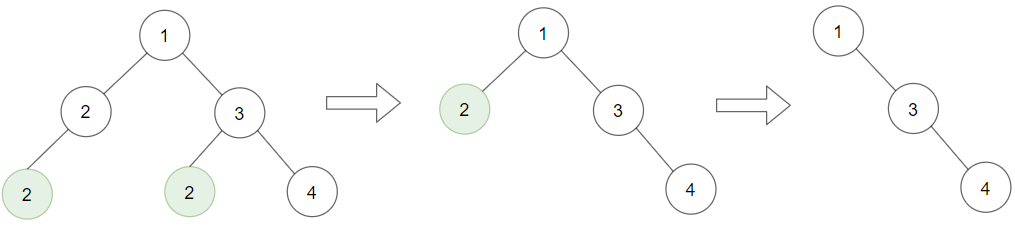
Input: root = [1,2,3,2,null,2,4], target = 2 Output: [1,null,3,null,4] Explanation: Leaf nodes in green with value (target = 2) are removed (Picture in left). After removing, new nodes become leaf nodes with value (target = 2) (Picture in center).
Example 2:
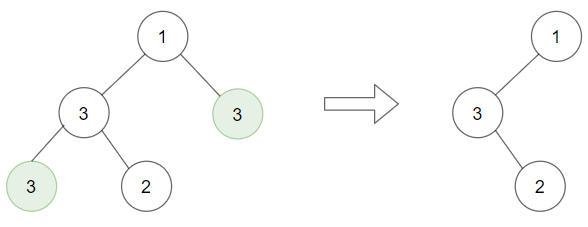
Input: root = [1,3,3,3,2], target = 3 Output: [1,3,null,null,2]
Example 3:
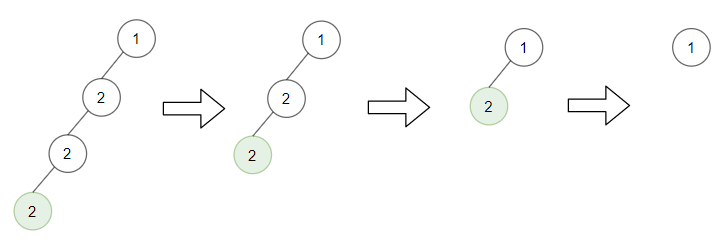
Input: root = [1,2,null,2,null,2], target = 2 Output: [1] Explanation: Leaf nodes in green with value (target = 2) are removed at each step.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3000]. 1 <= Node.val, target <= 1000
Solution
delete-leaves-with-a-given-value.py
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def dfs(self, root, target):
if not root: return None
root.left = self.dfs(root.left, target)
root.right = self.dfs(root.right, target)
if root.left == root.right == None and root.val == target: return None
return root
def removeLeafNodes(self, root: TreeNode, target: int) -> TreeNode:
return self.dfs(root, target)