2096. Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another


Description
You are given the root of a binary tree with n nodes. Each node is uniquely assigned a value from 1 to n. You are also given an integer startValue representing the value of the start node s, and a different integer destValue representing the value of the destination node t.
Find the shortest path starting from node s and ending at node t. Generate step-by-step directions of such path as a string consisting of only the uppercase letters 'L', 'R', and 'U'. Each letter indicates a specific direction:
'L'means to go from a node to its left child node.'R'means to go from a node to its right child node.'U'means to go from a node to its parent node.
Return the step-by-step directions of the shortest path from node s to node t.
Example 1:
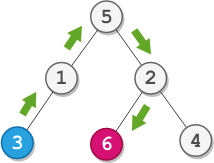
Input: root = [5,1,2,3,null,6,4], startValue = 3, destValue = 6 Output: "UURL" Explanation: The shortest path is: 3 → 1 → 5 → 2 → 6.
Example 2:
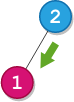
Input: root = [2,1], startValue = 2, destValue = 1 Output: "L" Explanation: The shortest path is: 2 → 1.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 2 <= n <= 1051 <= Node.val <= n- All the values in the tree are unique.
1 <= startValue, destValue <= nstartValue != destValue
Solution
step-by-step-directions-from-a-binary-tree-node-to-another.py
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def getDirections(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], startValue: int, destValue: int) -> str:
nodes = collections.defaultdict(tuple)
def go(node, parent):
if not node: return
nodes[node.val] = (parent, node)
go(node.left, node.val)
go(node.right, node.val)
go(root, -1)
deq = collections.deque([(startValue, "")])
visited = set([startValue])
while deq:
x, path = deq.popleft()
if x == destValue: return path
if x == -1: continue
parent, node = nodes[x]
if parent not in visited:
visited.add(parent)
deq.append((parent, path + "U"))
if node.left and node.left.val not in visited:
visited.add(node.left.val)
deq.append((node.left.val, path + "L"))
if node.right and node.right.val not in visited:
visited.add(node.right.val)
deq.append((node.right.val, path + "R"))