2385. Amount of Time for Binary Tree to Be Infected


Description
You are given the root of a binary tree with unique values, and an integer start. At minute 0, an infection starts from the node with value start.
Each minute, a node becomes infected if:
- The node is currently uninfected.
- The node is adjacent to an infected node.
Return the number of minutes needed for the entire tree to be infected.
Example 1:
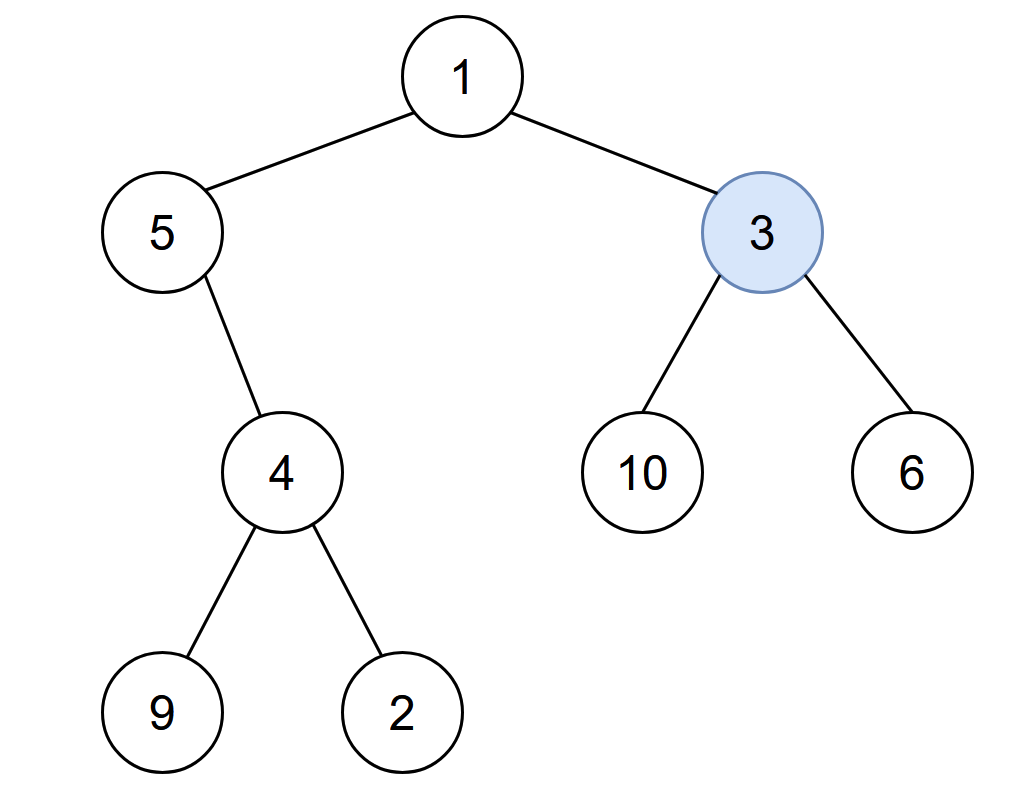
Input: root = [1,5,3,null,4,10,6,9,2], start = 3 Output: 4 Explanation: The following nodes are infected during: - Minute 0: Node 3 - Minute 1: Nodes 1, 10 and 6 - Minute 2: Node 5 - Minute 3: Node 4 - Minute 4: Nodes 9 and 2 It takes 4 minutes for the whole tree to be infected so we return 4.
Example 2:

Input: root = [1], start = 1 Output: 0 Explanation: At minute 0, the only node in the tree is infected so we return 0.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 105- Each node has a unique value.
- A node with a value of
startexists in the tree.
Solution
amount-of-time-for-binary-tree-to-be-infected.py
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def amountOfTime(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], start: int) -> int:
time = 0
graph = defaultdict(list)
N = 0
def dfs(node):
nonlocal N
if not node: return
N += 1
if node.left:
graph[node.left.val].append(node.val)
graph[node.val].append(node.left.val)
if node.right:
graph[node.right.val].append(node.val)
graph[node.val].append(node.right.val)
dfs(node.left)
dfs(node.right)
dfs(root)
if N == 1: return 0
s = [start]
visited = defaultdict(lambda : False)
visited[start] = True
while s:
nxt = []
for node in s:
for nei in graph[node]:
if not visited[nei]:
visited[nei] = True
nxt.append(nei)
time += 1
s = nxt
return time - 1